Matter In Our Surroundings
Matter is anything that has mass and occupies space. Everything we see—air, water, food, furniture—is made up of tiny particles. These particles are constantly in motion, have space between them, and attract one another with varying force. Matter exists in three physical states: solids, liquids, and gases, each with different properties based on the arrangement and movement of their particles.
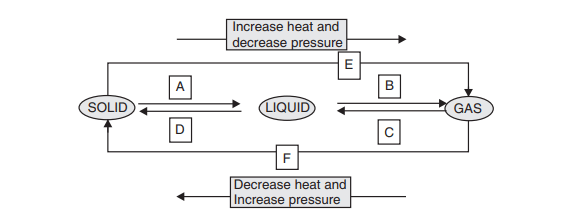
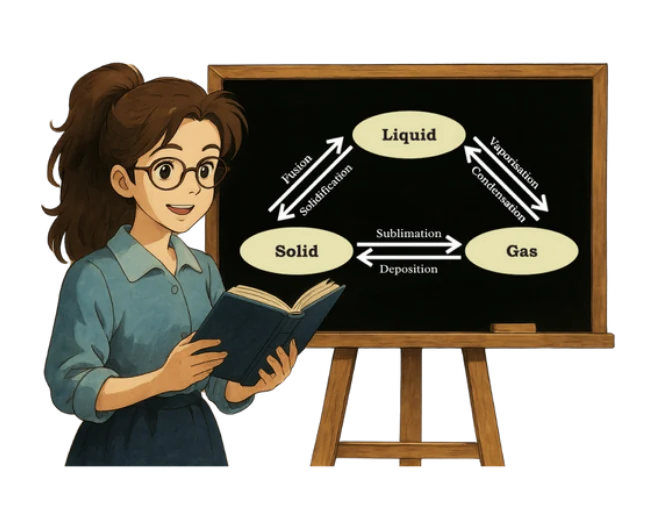
Matter can change from one state to another when temperature or pressure is altered. For example, ice melts to become water, and water boils to become steam. Some substances, like camphor, directly change from solid to gas — a process known as sublimation. Evaporation is another key concept, where liquids turn into gas below boiling point and cause cooling (e.g., sweat cooling the body). This chapter lays the foundation for understanding how matter behaves in our physical world.
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 1 – Matter in Our Surroundings (2025 Edition)
📄 Page 3 – 📗In-Text Questions
Chair, air, love, smell, hate, almonds, thought, cold, lemon water, smell of perfume.
Whereas love, smell, hate, thought, cold, and smell of perfume are emotions, feelings, or sensations. They do not have mass or volume, so they are not matter.Hence, only the substances that exist physically and have weight and volume are classified as matter.
The smell of hot sizzling food reaches you several metres away, but to get the smell from cold food you have to go close.
On the other hand, the smell from cold food spreads slowly because its particles have less energy and move slower.
So, the rate of diffusion increases with temperature, which is why we can smell hot food from far away.
Hence, the ability of a diver to move through water proves that there is inter-particle space in liquids, allowing movement.
- The particles of matter are very, very small.
- The particles of matter have spaces between them.
- The particles of matter are constantly moving.
- The particles of matter attract one another.
📄 Page 6 – 📗In-Text Questions
Air < Exhaust from chimneys < Cotton < Water < Honey < Chalk < Iron
| Property | Solid | Liquid | Gas |
|---|---|---|---|
| Shape and Volume | Solids have a fixed shape and a fixed volume. | Liquids have a fixed volume but they have no fixed shape. | Gases have neither a fixed shape nor a fixed volume. |
| Compressibility | Solids cannot be compressed much. | Like solids, liquids cannot be compressed much. | Gases can be compressed easily |
| Fluidity | Particles of solid cannot move freely. | These particles move freely. | Gaseous particles are in a continuous, random motion. |
| Particle packing | These particles attract each other very strongly. | The force of attraction between liquid particles is less than solid particles. | The force of attraction is least between gaseous particles. |
| Density | Solids have high densities. They are heavy. | Liquids have moderate to high densities. They are usually less dense than solids. | Gases have very low densities. They are very, very light |
- Rigidity: Rigidity refers to the property of a solid to resist change in its shape , when an outside force is applied. In most simple terms, rigidity means ‘stiffness’. The particles in a solid are very closely packed and there are very strong forces of attraction between them, so solids possess high rigidity. Liquids and gases are not rigid because the positions of their particles are not fixed.
- Compressibility: . Compressibility is the property of a fluid (or a solid) due to which its volume decreases when pressure is applied. The particles in gases have large spaces between them due to which their volume decreases too much when pressure is applied on them. So, gases have high compressibility. On the other hand, the particles in solids and liquids are closely packed, so solids and liquids do not have much compressibility.
- Fluidity: The property of flowing easily is called fluidity. Gases and liquids exhibit the property of fluidity, so they are called fluids. Due to large interparticle distances and very weak forces of attraction, gases can flow extremely easily. So, the gases have very high fluidity . And because of comparatively smaller interparticle distances and stronger forces of attraction between their particles, the fluidity of liquids is less than that of gases. Solids are not fluids, they have no fluidity.
- Filling a container: A gas fills its container completely because due to high kinetic energy and negligible interparticle forces of attraction, the particles in a gas move with high speeds in all directions and occupy all the space in the container.
- Shape: The external form or appearance of a substance is called its shape. A solid has a fixed shape because the particles in a solid are closely packed and their positions are fixed due to strong forces of attraction between them. The liquids and gases do not have fixed shapes because the positions of particles in them are not fixed due to comparatively weaker forces of attraction between them.
- Kinetic energy: Gas > Liquid > Solid.
The energy possessed by a material due to the motion of its particles is called kinetic energy. At a given temperature, the particles in a gas have the maximum kinetic energy because they move with high speeds due to weakest forces of attraction among them. Liquids have lesser kinetic energy (than gases) whereas solids have the the least kinetic energy at a given temperature. - Density: Generally Solid > Liquid > Gas.
The mass per unit volume of a material is called its density. Solids have high densities because their particles are very close together. Liquids have usually lower densities than solids because their particles are somewhat more loosely packed than that in solids. Gases have the lowest densities because their particles are very far apart from one another.
(a) A gas fills completely the vessel in which it is kept.
(b) A gas exerts pressure on the walls of the container.
(c) A wooden table should be called a solid.
(d) We can easily move our hand in air but not through a wooden block.
(b) Due to freely moving particles and high kinetic energy, particles of gas move randomly in all the directions and hit the walls of the container exerting pressure.
(c) A wooden table should be Solid Because it has a definite shape and fixed volume.
(d) Air is made of particles with a lot of space between them, so we can move our hand easily. In solids like wood, particles are tightly packed, so it's hard to pass through without great force.
📄 Page 9 – 📗In-Text Questions
(a) 300 K − 273 = 27 °C
(b) 573 K − 273 = 300 °C
(b) At 100°C, water is at its boiling point, so it exists as liquid and gas both — it starts converting from liquid to steam.
For example, a solid melts on heating. Its temperature does not rise until the entire solid is converted into liquid. This heat energy gets hidden into the content and is known as the latent heat.
📄 Page 10 – 📗 In-Text Questions
📄 Page 12 – 📘 Exercise Question
(b) 470 K − 273 = 197 °C
(a) 25 °C + 273 = 298 K
(b) 373 °C + 273 = 646 K
(a) Naphthalene balls disappear over time without leaving any solid.
(b) We can smell perfume sitting several metres away.
(b) The particles of perfume diffuse into the air and spread in all directions. Since particles of gases move fast, the smell reaches us even if we are far away.
(i) oxygen is a gas, so it has the weakest forces of attraction between its particles.
(ii) water is a liquid, so it has stronger forces of attraction between its particles (than oxygen).
(iii) sugar is a solid, so it has the strongest forces of attraction between its particles.
Thus, the increasing order of forces of attraction between the particles of water, sugar and oxygen will be : Oxygen < Water < Sugar
(a) 25°C ? (b) 0°C ? (c) 100°C ?
(b) At 0°C, water exists as solid and liquid both (melting point).
(c) At 100°C, water exists as liquid and gas both (boiling point).
(a) Water at room temperature is a liquid.
(b) An iron almirah is a solid.
(i) water has a fixed volume (which does not change on changing its container).
(ii) water has no fixed shape (it takes the shape of the container in which it is kept).
(b) The two general properties of solids are that solids have ‘a fixed shape’ and ‘a fixed volume’. An almirah is a solid at room temperature because :
(i) an almirah has a fixed shape (which cannot be changed by pressing it with hands).
(ii) an almirah has a fixed volume (which depends on the dimensions according to which it is made).